The atom is the smallest unit of matter composed of three sub-atomic particles: the proton, the neutron, and the electron. The atom's nucleus, a dense, positively charged core of protons and neutrons, is surrounded by a negatively charged electron cloud. [1]
Parts of an Atom
1. Electron
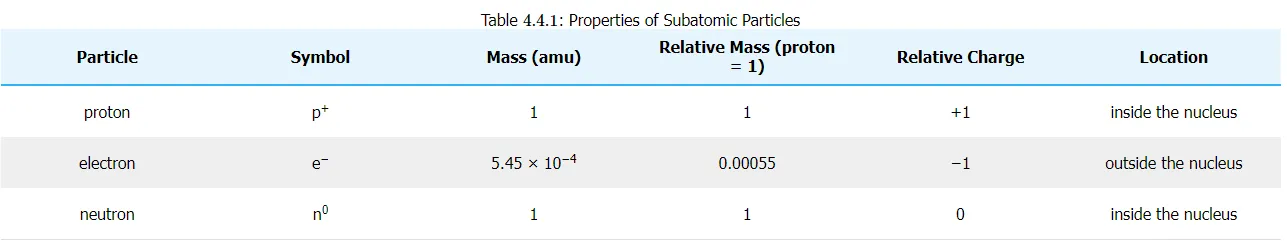
Electrons are one of three main types of particles that make up atoms. They are a type of fundamental particular called leptons. All leptons have an electric charge of -1 or 0. Electron are very tiny particles. The mass of an electron is only about 1/2000 the mass of a proton or neutron, so electron contribute virtually nothing to the total mass of an atom. The electric charge of an electron is -1, which is equal to but opposite from the charge of a proton(+). Since there are exactly as many electrons as protons in every atom, the positive and negative charges "cancel out," making the atom electrically neutral.
Unlike protons and neutrons, located inside the nucleus at the center of the atom, electrons are found outside the nucleus. Because opposite electric charges attract one another, negative electrons attract positive nucleus. This force of attraction keeps electrons constantly traveling across the otherwise vacant area around the nucleus.
2. Proton
Proton is one of the three primary components of an atom. Atoms contain protons in their nucleus. A tiny, dense area at the center of the atom. Protons have a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (amu), or around 1.671027 kilograms, and a positive electrical charge of 1 (+1), making them positively charged particles. Along with neutrons, they make up approximately all of the mass of an atom.
3. Neutrons
Atoms of all elements except the hydrogen atom have neutrons in their
nucleus. Neutrons are electrically neutral, as opposed to the
electrically charged protons and electrons. The neutrons are designated
as n0 in the diagram above as a result. Zero charges are represented by
zero. One atomic mass unit is equal to the mass of a proton, although
the mass of a neutron is slightly higher (amu). The diameter of a
neutron is roughly 1.71015 meters, which is the same as proton. An
atomic mass unit is equal to approximately 1.671027 kilograms.
The neutron is neutral, as you could have inferred from its name. It is
neither drawn to nor drawn away from other objects because it carries no
charge at all. With one exception, every atom contains neutrons, coupled
with other neutrons and protons in the atomic nucleus.